The Most Important Recommendations
Table of Contents
- Optimized blocks
- Data type VARIANT
- Program blocks
- Multi-instances
- Reusability of blocks
- Symbolic addressing
- ARRAY data type and indirect addressing
- Access to I/O areas with PLC data types
- Libraries
- No bit memory but global data blockss
- References
Optimized Blocks
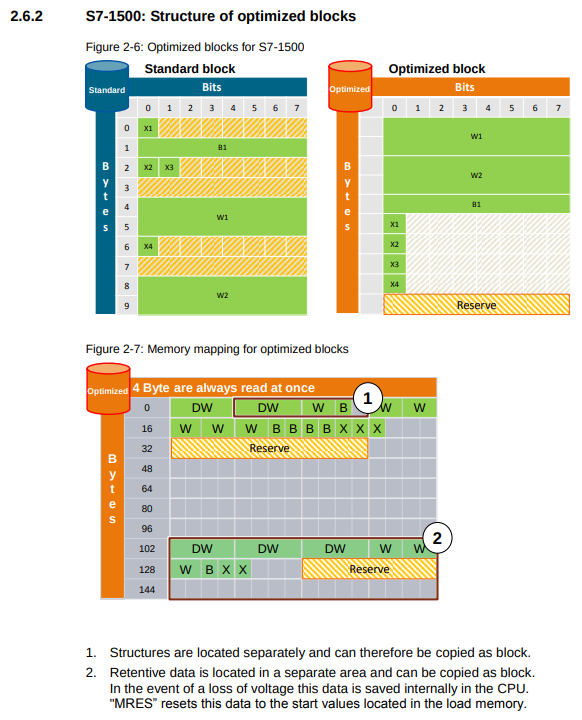
storage reserve
Optimized blocks have a storage reserve for loading in running operation
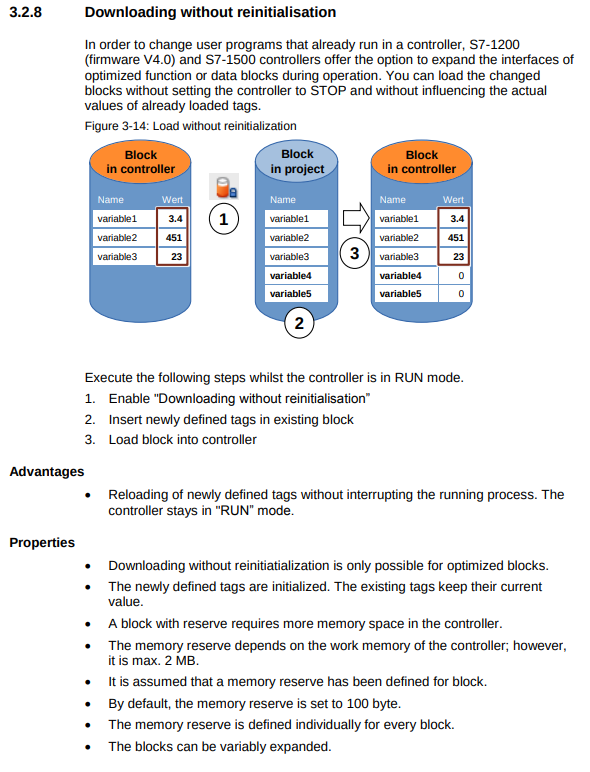
Example use case for "downloading without reinitialisation"
Define a memory reserve for blocks that are to be expanding during commissioning. The commissioning process is not disturbed by a download since the actual values of the existing tags remain.
Recommendation
optimized blocks
- In general, only use optimized blocks.
- You do not require absolute addressing, and you can always address with symbolic data (object-related). Indirect addressing is also possible with symbolic data.
- Process optimized blocks in the controller is considerably faster than for standard blocks
- Avoid the copying/assigning of data between optimized and non-optimized blocks. The data conversion required between source and destination format requires high processing time.
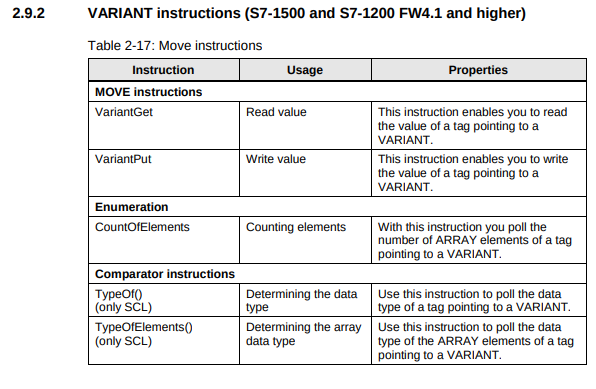
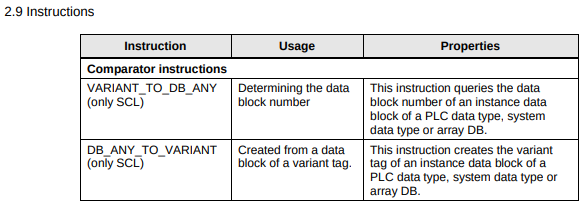
Data type VARIANT
Recommendation
VARIANT
- In general, there is no longer a need to employ the ANY pointer.
- Use the data type VARIANT only for indirect addressing when the data types are only determined at runtime.
- Use the data type VARIANT as InOut formal parameter to create generic blocks that are independent of the data type of the actual parameters.
- Use the VARIANT data type has an integrated type test, therefore errors are detected early. Symbolic address is easier to interpret what the code is doing
- The VARIANT instruction can be used for type identification
- Use the index for arrays rather than addressing the array elements via ANY
Program Blocks
Help you to...
Structure the program clearly and well
Recommendation
Program Blocks
- Structure your automation task.
- Break up your program into areas, functional units, sub-function units. Divide until you get functions that you can use several times with different parameters.
- Specify the interfaces between function units. Define the unique interfaces for functionalities that are delivered by "external companies"
Multi-instances
Recommendation
Use multiple-instances in order to...
- reduce the number of instance DBs.
- create reusable and clear user programs.
- program local functions, for example, IEC Timer blocks , IEC Counter blocks, edge evaluation
Reusability of blocks
If you want to reuse the block, please note the following recommendations:
- Always look at blocks as encapsulated functions. I.e. each block represents a completed partial task within the entire user program.
- Use several cyclic Main OBs (Software Units) to group the plant parts.
- Always execute a data exchange between the blocks via its interfaces and not via its instances (chapter 3.4.1 Block interfaces as data exchange).
- Do not use project-specific data and avoid the following block contents:
- Access to global DBs and use of single-instance DBs
- Access to tags
- Access to global constants
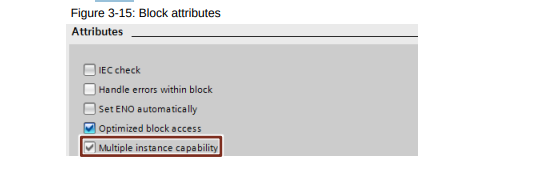
- Reusable blocks have the same requirements as know-how-protected blocks in libraries. This is why you have to check the blocks for reusability based on the "Multiple instance capability” block property. Compile the block before the check.
Symbolic addressing
Recommendations
- "Don’t worry about the storage of the data”
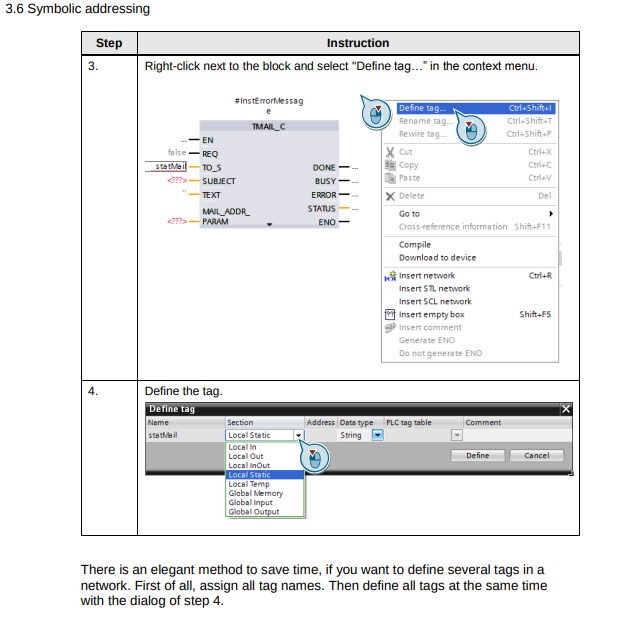
- "Think” symbolically. Enter the "descriptive” name for each function, tag or data, such as, for example, Pump_boiler_1, heater_room_4, etc. Thus a created program can be simply read, without requiring many comments.
- Give all the tags used a direct symbolic name and define them afterwards with a right-click.
ARRAY data type and indirect addressing
Recommendation
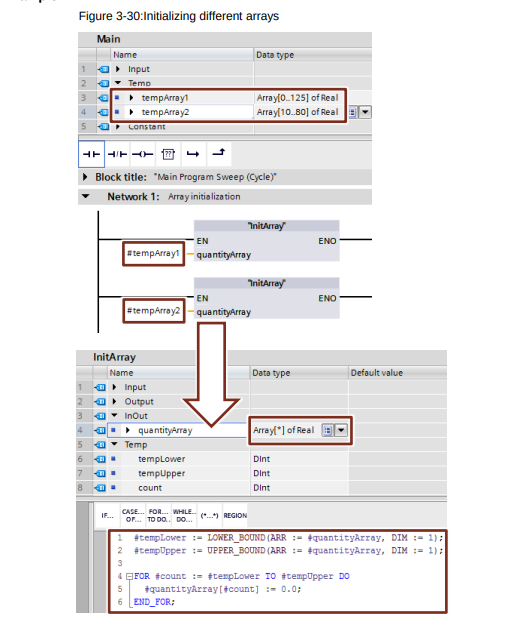
- Use ARRAY for indexed accesses instead of pointer (e.g. ANY pointer). This makes it easier to read the program since an ARRAY is more meaningful with a symbolic name than a pointer in a memory area.
- When calculating an index at runtime employ a DINT data type as temporary tag for highest performance. As memory is accessed 4 bytes at a time.
- Use the "MOVE_BLK” instruction to copy parts of an ARRAY into another one.
- Use the "GET_ERR_ID” instruction to catch access errors within the Array.
Formal parameter array[*] ^V14
Optimized blocks which do not contain STL can employ the variable length array formal parameter Array[*]
In the code the lower and upper bounds of the index can be found with the LOWER_BOUND(ARRAY, DIMENSIONS) and UPPER_BOUND(ARRAY, DIMENSIONS) instructions
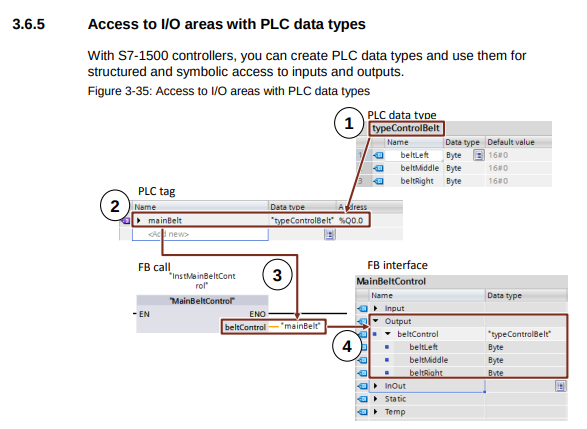
Access to I/O areas with PLC data types
Recommendation

Libraries
Recommendation
- Create the master copies for easy reusability of blocks, hardware configurations, HMI screens, etc.
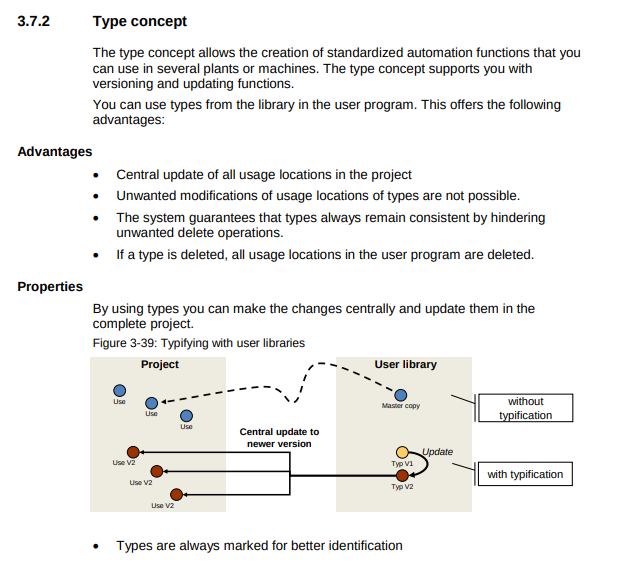
- Create the types for the system-supported reusability of library elements:
- Versioning of blocks
- Central update function of all usage locations
- Create the types for the system-supported reusability of library elements:
- Use the global library for the exchange with other users or as central storage for the simultaneous use of several users.
- Configure the storage location of your global library so it can automatically be opened when starting the TIA Portal.
Type Concept
No bit memory but global data blocks
Recommendation
- Always use optimized global DBs, instead of bit memory, (system, counters, timers, clock memory). As, bit memory is not optimized for backward compatibility reasons. And system memory is controller specific.